As TERC celebrates more than 55 years in STEM education, we are especially grateful to our founder, Arthur H. Nelson, who passed away in 2015.
Nelson was a noted entrepreneur, passionate about innovation, technology, and education. He led the organization in its early days and served as Chairman of the Board of Trustees until 2013. Originally, the acronym TERC stood for Technical Education Research Centers—a title that encompassed the technical and vocational education endeavors of the organization at the time. We’ve come a long way since then. Now we are solely known as TERC, and our project research and development extend across all areas of STEM education, serving K-12 classrooms, museums, afterschool programs, community colleges, adult education centers, universities, and other research institutions.
Organizational Structure
TERC comprises a dedicated team of approximately 90 staff members based all around the United States. Approximately 60 percent of these staff members hold advanced degrees across a range of disciplines, and many of them have achieved national and international recognition for their contributions to their individual fields as well as educational research, curriculum development, and professional development. We share the common goal of transforming STEM education, making STEM more accessible to all learners, and igniting passion for lifelong learning.
TERC History

Beginning in occupational education for state and local agencies, evaluations developed into a fundamental TERC service through the years. Currently, TERC’s STEM Education Evaluation Center (SEEC) offers external evaluation services and consultations for the STEM education sector.
LEARN MORE
As laser technology expands there became a need for a training program for technicians. TERC develops the first program for training laser-electro optic technicians.
In 1973, TERC expanded from its base in Cambridge to open satellite offices in locations around the United States, including Waco, Texas and Washington, DC.
In 1974, Jimmy Carter became chair of the DNC and announced his candidacy for president in December 1974. He spent the next two years touring around the country meeting many people. One stop on his itinerary included TERC’s headquarters!
TERC’s first major publication was a groundbreaking 450-page sourcebook paired with a 50-state resource directory.
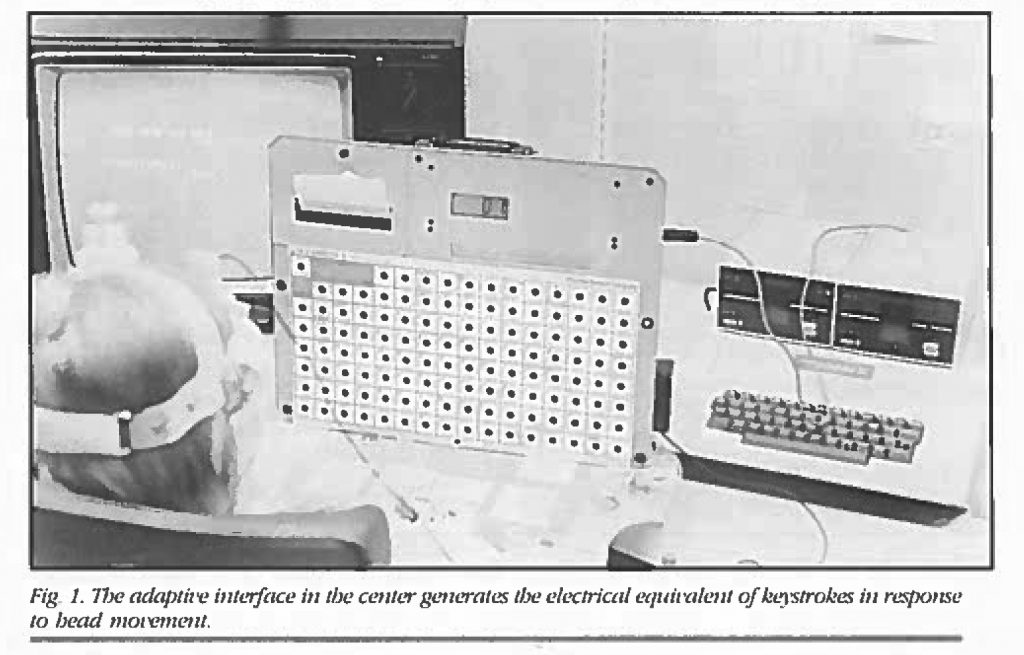
TERC’s Special Needs Center concentrated on equity in education and training for underserved populations—handicapped students, women in nontraditional occupations, and minority students. Research and development projects involved school industry collaborative planning, provisions of handbooks and in-service training for educators, and evaluations of compliance with nondiscrimination regulations.

The magazine continues to provide TERC staff an outlet to describe their current work to a larger audience.
TERC staff spent two years conducting a national project to find out what could be done about women’s low participation in male-intensive occupations. Through many interviews with coordinators of programs that recruited, trained, and placed women in skilled and technical jobs, researchers learned what to do and not to do to promote women’s success. They compiled their suggestions into two books containing guidelines for programs in non-traditional occupations (NTO), from planning to follow-up, and tested the guidelines at five post-secondary vocational and technical schools. The results were remarkable: 372 women enrolled in male-intensive occupational programs, and the programs enjoyed an excellent retention rate. All five NTO program coordinators were rehired by their schools with inside funding after the end of the TERC-funded field test.

TERC pioneered the use of microcomputers, telecommunications, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in the classroom, leading to the development of curriculum and professional programs by TERC (e.g., NGS Kids Network, Global Lab) and many other organizations that engage students in scientific investigations — collecting and analyzing data as they research questions in the physical, life, and Earth sciences.

Prior to the 1989 release of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics Curriculum and Evaluation Standards for School Mathematics, TERC began developing
Used Numbers — a series of curriculum units that focus on data analysis in grades K-6. This publication marked the beginning of TERC’s later curriculum Investigations.
The Kids Network Project represented a new kind of partnership between education, business, and government. Students worked in teams to decide how to collect data and determine its accuracy. After collecting and evaluating data, the students broadcast their findings over the National Geographic Kids Network, an international telecommunications network allowing students to conduct science research in their communities and share their findings with other students and professional scientists. Students in more than 8000 classrooms in 28 countries used the Kids Network.
LabNet established student research projects as an important and accepted part of science instruction throughout the United States by enhancing science teachers’ ability to involve students in science investigations. LabNet’s creators understood that high school science teachers, especially those in small or rural communities, are typically more isolated than other teachers simply because their numbers are so few. LabNet promoted interaction among science teachers – giving motivation and support to do experimental collaborative, project-based instruction, using technology as appropriate.
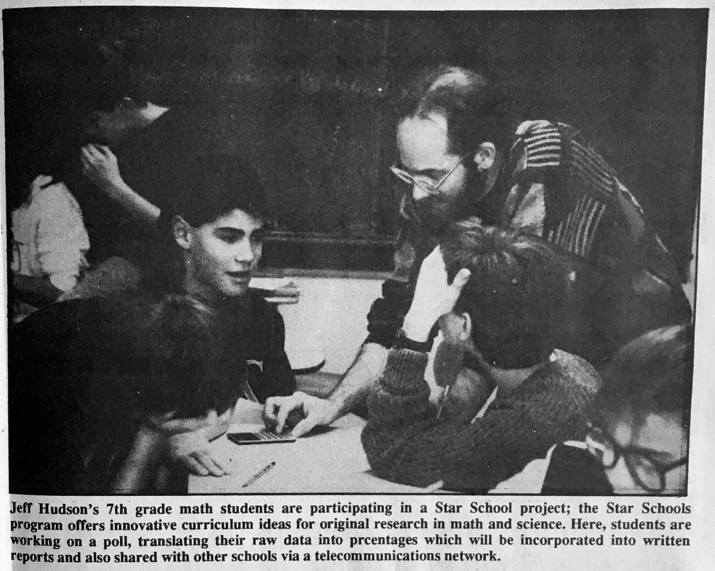
The Star Schools program was funded as an innovative, hands-on mathematics and science curriculum that encouraged critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration. The program brought technological tools into the classroom for exploration and problem solving.

TERC’s research on statistical reasoning and how computers could help students see and analyze data led to the development of software tools such as Tabletop — a graphical data analysis and visualization tool.
Not only is this NSF’s first climate change curriculum but also the first climate change education grant awarded by NSF. An international network of schools participated in activities designed by TERC to help students use tele-collaboration to expand their scientific investigations beyond the classroom walls and into the world.

Needing space to accommodate growing programs and staff, TERC relocated to the renovated carriage factory space in Cambridge where we still reside.

Investigations is a comprehensive math curriculum for grades K-5, designed to engage students in making sense of mathematical ideas. Several key goals guide the development of the curriculum, including communicating mathematics content and pedagogy to teachers.
PSL was a project that developed data-collection sensors and software on IBM PCs, building on TERC’s experiences with the ground-breaking MBL (Microcomputer-based Lab) project. It brought in a talented team of newcomers who became important in TERC’s work building software, curriculum, and teacher professional development using the PSL system.
TERC played a key role in the development of the teacher professional development for this NSF initiative and in the development of the first Massachusetts math and science standards. PALMS was a 5-year effort to improve the teaching and learning of math and science in Massachusetts schools.

The ViEW (Video for Exploring the World) project developed the CamMotion software, which allowed students to explore the mathematics of motion by creating and analyzing videos of their own movements, such as doing a cartwheel, jumping rope or riding a bike. The project was significantly ahead of its time, as video was analog – not digital – in the early 1990’s, so the first step in analyzing a video was to use a special “digitizer” to translate the video into machine-readable form. Then students used CamMotion to trace the position of a chosen point (e.g. their right hand) through consecutive frames, creating a trace of its motion over time, which was superimposed on a frame of the video. The software could then create graphs of x- or y-position over time, as well as calculate velocity. The system thus tied traditional physics and math representations to students’ embodied knowledge.
Located at TERC from 1995-2005, the Regional Alliance for Mathematics and Science Education was the Northeast and Islands Eisenhower Regional Consortium serving CT, ME, MA, NH, NY, PR, RI, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and VT. Funded by the U.S. Department of Education, the Regional Alliance was part of a national network comprising ten Eisenhower Regional Consortia and the Eisenhower National Clearinghouse. The mission of the Regional Alliance was to support K-12 mathematics and science improvement efforts by disseminating information about high quality mathematics and science materials and providing technical assistance and professional development for teachers, administrators, and state education officials focused on improving mathematics and science teaching and learning.

TERC’s award-winning puzzle game continues to engage players using computational thinking skills.
LEARN MORE

This research group has built a body of evidence that continues to challenge long-standing, historically structured deficit conceptions of the academic abilities, life experiences, and developmental trajectories of students from non-dominant communities.
LSC-Net, a web-based, interactive community, enriched the work of Local Systemic Change (LSC) initiatives throughout the country and supported collaboration among them. Three virtual conferences that addressed sustainability of systemic change came out of this project resulting, in the development of MSPnet.
Science in Education became the first fully online master’s degree program for science teachers. It was designed for teachers, curriculum specialists, and instructional resource persons responsible for K-8 science education. The program aligned with National Science Education Standards, emphasizes inquiry-based science and introduces innovative, learner-centered teaching strategies. LEARN MORE

Global Lab launches students in grades 6–9 on a collaborative scientific enterprise. Students choose a local “study site” for interdisciplinary, hands-on explorations in four essential areas: interaction of matter and energy; bio-geochemical cycles; biomes and biodiversity; and Earth as a system.
Global Lab includes curriculum guide, 5 units (teacher and student books), instruments and supplies, and a network membership. The Investigating Science Outdoors eBooks developed by TERC are based on Global Lab.

MSPnet is an electronic learning community for the National Science Foundation’s Math, Science, Partnership (MSP) Program. With the MSP program, the National Science Foundation implemented an important facet of the President’s No Child Left Behind (NCLB) vision for K-12 education.
LEARN MORE

Investigating Astronomy is the first comprehensive astronomy textbook written specifically for high school students.
LEARN MORE
This research and development program was founded on the conviction that students can and should experience the life sciences as dynamic fields of inquiry whose diversity reflects the immense diversity of living systems.
LEARN MORE

This full-year integrated science curriculum weaves its way through the disciplines of biology, chemistry, physics, astronomy, and Earth science, as well as sociology, ethics, and the psychology of human thought and behavior.
LEARN MORE
TERC and educational software developers at Vcom3D used SigningAvatar accessibility software to develop an interactive 3D dictionary of science terms and definitions to support access to standards-based science content among elementary and middle-grade students who are deaf or hard of hearing and whose first language is sign. The project continues to evaluate the extent to which use of the dictionary furthers understanding of science content, interest in science, and the ability to study independently. As the project evolves, it seeks to create a more robust sign/facial expression/body space library for use in developing subsequent volumes of the dictionary or in SigningAvatar-enabling other science materials.

This year-long, project-based high school curriculum that situates standards-based science learning in authentic workplace contexts. The curriculum is based on the principle that all students learn better and more deeply when they learn in context, and on the belief that such an approach offers students who have not been engaged by abstract science the opportunity to achieve on a par with their peers.
LEARN MORE
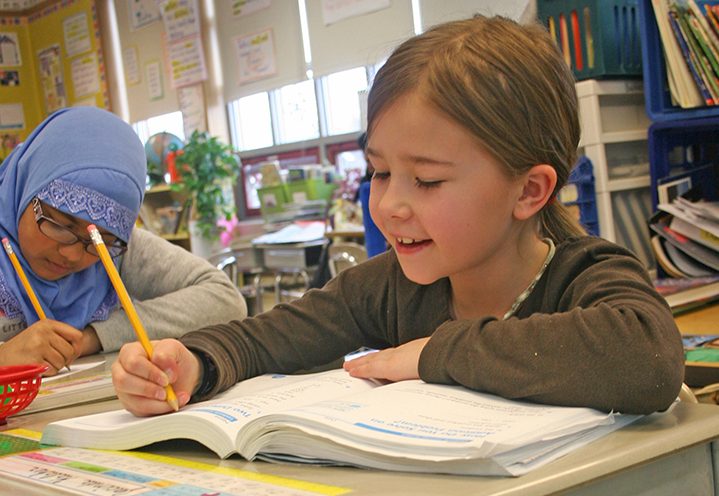

Between periods of development, Investigations focuses on supporting educators committed to improving the teaching and learning of elementary mathematics. The components of the Second Edition include a variety of features that address: professional development, early algebra, the range of learners, practice and review, and resources for families.

EMPower is a mathematics curriculum for non-traditional students enrolled in adult basic education, pre-GED, GED, and transitional courses to college, as well as students in alternative high schools, workplace settings, or corrections programs.
LEARN MORE
TERC partners with environmental action groups in twelve states to advance the quantitative literacy skills needed to understand and solve pressing environmental problems. Statistics for Action (SfA) builds on TERC’s research in adult numeracy and helps situate significant math learning in meaningful, accessible contexts: namely, the community centers, public institutions, and homes where concerned citizens gather to examine local environmental and public health data.
LEARN MORE

Students and astronauts use this powerful new tool to explore earth from space.

A research design and development team continues to investigate the possibilities—and challenging the assumptions—of game-based learning environments.
LEARN MORE

An 86-page full-color book, Mixing in Math contains mathematical activities with fun instructional pictures, all of which are connected to Common Core State Standards.

TERC, in partnership with the Girl Scouts of Eastern Massachusetts and 360KID (a children’s media company), spearhead the Girls’ Energy Conservation Corps (GECCo), an innovative new media project that engages girls ages 8-11 in energy conservation activities.
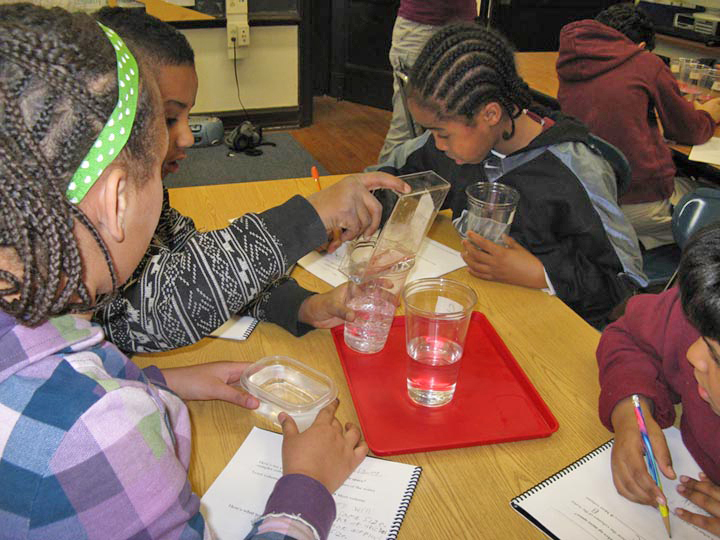

The Inquiry Project stems from a partnership between TERC and Tufts University. The project offers content and strategies to help elementary teachers lay the groundwork for molecular theory studies in junior high and high school by teaching concepts such as weight, volume, and density in grades 3-5.

A Kickstarter campaign with a $50,000 goal to help fund new desktop versions of the game allowed fans of the 1990s release help bring the reboot to life, raising $101,716.
TERC revised and enhanced its groundbreaking mathematics curriculum for adult learners. The updated and enhanced versions of three titles (Using Benchmarks, Split It Up, and Everyday Number Sense) in the original EMPower™ series. EMPower Plus titles, as well as the original series, align with Career and College Readiness Standards for Adult Education.

This event showcased cutting-edge NSF-funded work to improve teaching and learning and allowed colleagues affiliated with MSPnet, CADRE, CIRCL, CAISE, STELAR, CS10K Community, and ARC to view, discuss, and comment on each other’s work. The showcase also allowed members of each project to disseminate their work to the public at large, helping NSF achieve its goal of broad dissemination of innovative work. The Video Showcase continues to expand each year through 2019.
The culmination of over 25 years of research and development aimed at improving the teaching and learning of elementary mathematics, Investigations 3 maintains and builds on the philosophy and pedagogy of the first and second editions, and continues to be based on the work of real teachers and students. Investigations 3 is a focused, coherent, and rigorous K-5 mathematics curriculum, fully aligned to the content and practice standards of the Common Core State Standards (CCSS)
Investigations 3rd edition


As TERC continues to grow, the brand is updated to reflect the organizations core values. A new website is developed along with a new logo, typeface, tagline, and imagery.

Six new signing glossary apps were developed to help families with deaf or hard of hearing members access information in aquariums, botanical gardens, natural history museums, nature centers, science museums, and zoos. The apps provide access to thousands of signed terms and definitions, and are free to use on iPhone and Android mobile devices.

This online community, funded by the National Science Foundation, provided teacher leaders, researchers and administrators with resources, networking tools and interactive events to explore topics related to STEM teacher leadership. Members shared their leadership paths, challenges, strategies, resources, upcoming opportunities and events with each other. The site also provided a platform to improve STEM teaching and learning within schools, contribute to new research and development efforts, and influence education policy. The network had over 3,000 members.
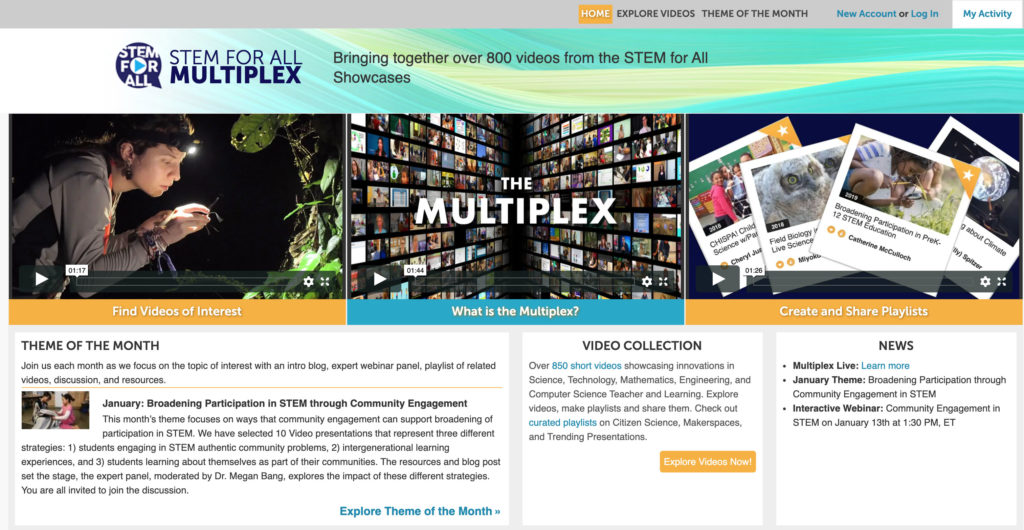
The Multiplex, funded by the National Science Foundation, provided access to over 1,000 videos showcasing federally funded research and development projects in STEM education. It enabled researchers, educators, policymakers and parents to interact with each other, view and discuss cutting-edge efforts to improve STEM education, and create and share playlists. The site also hosted “Theme of the Month” events featuring expert panel webinars and online asynchronous discussions.

In conjunction with researchers at the University of Texas at Austin and the University of Wisconsin-Madison, TERC developed LEAP, a supplemental program entirely focused on building early algebra thinking. TERC partnered with Didax to publish the instructional materials for the LEAP curriculum.
LEARN MORE

Storytelling Math from Charlesbridge Publishing celebrates math, diversity, and the power of storytelling. The books feature children using math in their daily adventures as they play, build, and discover the world around them. Joyful stories and hands-on activities make it easy for kids and their grown-ups to explore everyday math together. Storytelling Math is led by Marlene Kliman at TERC.
LEARN MORE

A complete turnkey classroom version of Zoombinis is released, in collaboration with FableVision Games, with the capability for teachers to track their students’ progress and assessment.
LEARN MORE

Walch Education and TERC announce a new partnership to offer TERC’s highly-respected EMPower™ and EMPower™ Plus series. EMPower and EMPower Plus address the tremendous need for adult students to develop a strong conceptual foundation that supports the achievement of higher-level math skills. The series was written by adult education professionals, field-tested in adult education programs, and is aligned with the College and Career Readiness Standards for Adult Education (CCRSAE).
LEARN MORE

The National Science Foundation selected TERC to host and lead the new Reimagining Equity and Values in Informal STEM Education (REVISE) Center, a new equity resource center. This Center seeks to expand the foundational work conducted by the Center for Advancement of Informal Science Education (CAISE) to enhance access and equity-centered practices in informal STEM education (ISE).
LEARN MORE
